Introduction
Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) have become essential tools for businesses across various industries. The choice of technology is crucial for the success of an RTLS deployment. Ultra-wideband (UWB), Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), and BLE Angle of Arrival (AoA) are the primary technologies employed in RTLS solutions. This blog delves into the fundamentals of these technologies, their key differences, and their optimal use cases.
Understanding the Technologies
- UWB: Utilizes short-range, low-power radio waves with a wide bandwidth for precise distance measurements. It offers centimetre-level accuracy through Time of Flight (ToF) or Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA) techniques.
- BLE: A wireless communication protocol designed for low power consumption. While less accurate than UWB, it provides a longer range and is widely adopted. Primarily relies on the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) for distance estimation.
- BLE AoA: An extension of BLE that measures the angle of arrival of a signal at multiple antennas, enhancing location accuracy compared to traditional RSSI-based BLE.
Key Differences
| Feature | UWB | BLE | BLE AoA |
| Accuracy | Centimeter-level | Meter-level | Sub-meter level |
| Range | Shorter range | Longer range | Shorter range |
| Power Consumption | Higher | Lower | Lower |
| Cost | Generally higher | Lower | Higher than BLE |
| Complexity | Higher | Lower | Higher than BLE |
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Use Case
The optimal technology for an RTLS solution depends on the application’s specific requirements.
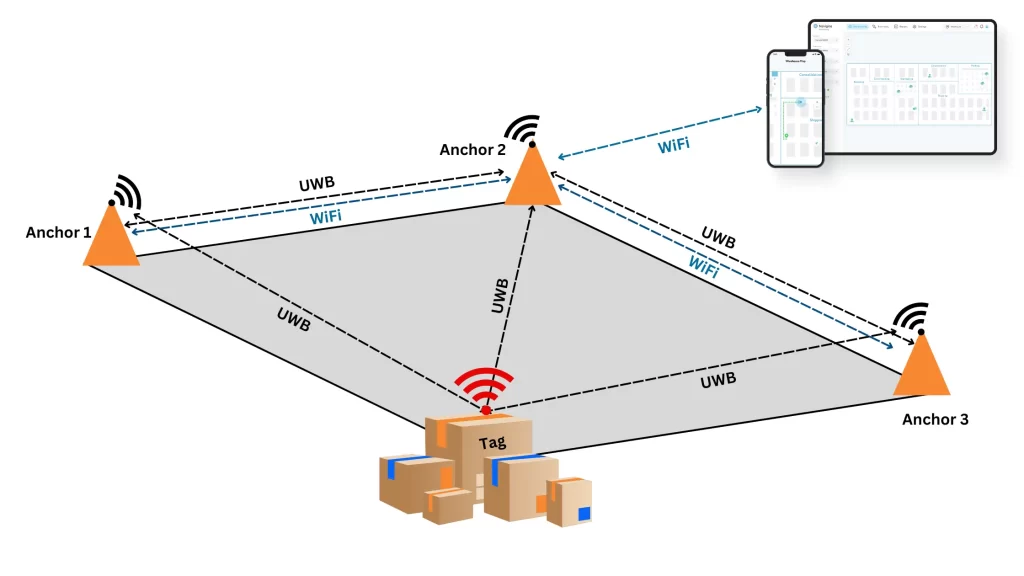
When to Use UWB:
- High accuracy: Applications demanding precise location data, such as asset tracking in high-value environments (e.g., healthcare, logistics), automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and robotics.
- Challenging environments: Areas with metal structures, obstructions, or multipath interference where UWB can penetrate obstacles is advantageous.
- Long range: Scenarios requiring extended coverage, though BLE may also be suitable in certain cases.
- High security: Applications handling sensitive data due to UWB’s strong encryption and anti-spoofing capabilities.
When to Use BLE:
- Lower cost: Applications with budget constraints or large-scale deployments where cost-efficiency is a priority.
- Wide coverage: Scenarios requiring broader indoor coverage, such as people tracking in retail stores or office buildings.
- Lower accuracy: Applications with sufficient approximate location information, like proximity marketing or basic asset tracking.
- Power efficiency: Devices with limited battery life or those deployed in remote locations.
- Existing infrastructure: If a BLE network is already in place, leveraging it for location-based services can be cost-effective.
When to Use BLE AoA:
- Improved accuracy: Applications requiring higher accuracy than standard BLE but where the cost of UWB is prohibitive.
- Indoor positioning: Scenarios demanding sub-meter level accuracy, such as indoor navigation or asset tracking in medium-value environments.
- Balance of accuracy and cost: Applications where a compromise between high accuracy and affordability is necessary.
Conclusion
UWB, BLE, and BLE AoA each offer unique advantages and are suitable for different RTLS applications. By carefully considering the specific requirements of your project, you can select the optimal technology or a combination of technologies to achieve your desired outcome. A thorough understanding of these technologies is essential for making informed decisions and maximizing the return on investment in your RTLS solution.
Let us help you harness the power of Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS). Our expertise lies in selecting the ideal technology and crafting a customized solution to elevate your business operations.
For more information on technology insights and services, please contact Intelloger.
Recent Posts
- Intelloger Partners with Cubic to Drive Digital Transformation for Banking & Financial Institutions
- Intelloger Partners with Acterys to Drive Agile Business Planning, Advanced Analytics, and Innovation
- Intelloger and AI.S2 Partner to Elevate and Streamline AI-Powered Demand Forecasting Solutions
- 6 Proven and Effective Steps to Improving the Financial Close Process with Oracle Solutions
- Top Innovative Trends Transforming Oracle Supply Chain Management (SCM) in 2025




