In today’s ever-changing tech landscape, the need for real-time data processing is higher than ever. This demand has given rise to a game-changing concept known as Edge Computing. In this article, we’ll explore what Edge Computing is and its various practical uses.
1. What is Edge Computing?
Edge Computing is a new way of computing that shifts away from the traditional centralized data processing model. In this approach, computation, data storage, and application functions are moved closer to where the data is generated or where the end-users are, often at the edge of the network. This decentralization significantly reduces the time data takes to travel to a distant data centre and back, minimizing delays and enhancing real-time processing.
Key Components of Edge Computing:
- Edge Devices: These are the endpoints where data is generated or used, such as IoT sensors, smartphones, autonomous vehicles, and industrial machinery.
- Edge Servers or Gateways: These act as intermediaries between edge devices and the cloud. They perform initial data processing, aggregation, and filtering before sending selected data to central data centres.
- Edge Data Centers: These are local or regional facilities equipped with computing resources and storage infrastructure that process and store data close to the source.
2. Use Cases of Edge Computing:
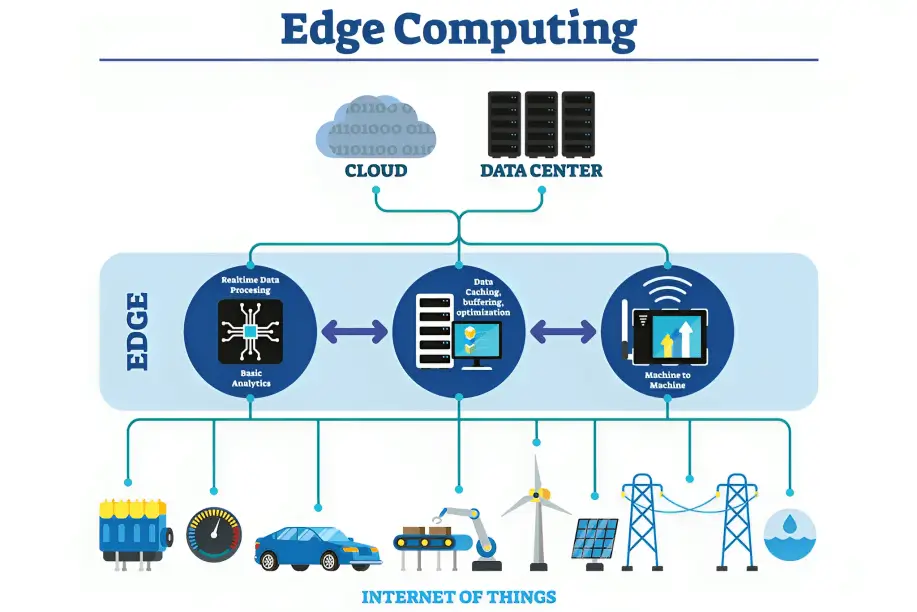
a. IoT and Smart Devices:
One of the primary applications of Edge Computing is in the Internet of Things (IoT). By placing edge servers near IoT devices, processing can be done locally, reducing the need to send all data to the cloud. This is vital for applications like smart homes, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring where immediate responses are crucial.
b. Autonomous Vehicles:
Edge Computing plays a key role in the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles. By processing sensor data locally within the vehicle or at the edge of the network, critical decisions can be made within milliseconds, ensuring passenger and pedestrian safety.
c. Telecommunications and 5G Networks:
The demand for low-latency services has surged with the advent of 5G. Edge Computing allows telecom operators to set up mini data centres at cell tower sites, reducing latency for services like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and online gaming.
d. Retail and Customer Experience:
In the retail sector, Edge Computing enables personalized in-store experiences. By analyzing customer behaviour and preferences in real-time, retailers can offer targeted promotions and recommendations.
e. Healthcare and Telemedicine:
Edge Computing empowers telemedicine by enabling real-time patient monitoring and providing instant feedback to healthcare professionals. This is invaluable for remote patient care and emergencies.
f. Smart Cities and Infrastructure:
Edge Computing supports the development of smart cities by enabling efficient traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety applications. Localized data processing ensures quick response times for critical services.
g. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
Edge Computing optimizes content delivery by caching content closer to end-users, reducing load times, and enhancing the user experience for web applications, streaming services, and online gaming.
In conclusion, Edge Computing is set to revolutionize how we process and analyze data. By making use of its capabilities, industries can achieve higher efficiency, reliability, and real-time responsiveness. From IoT to autonomous vehicles and beyond, Edge Computing offers diverse and far-reaching applications, promising a future where proximity is power.
Contact Intelloger for more information on technology insights and services.
Recent Posts
- 6 Proven and Effective Steps to Improving the Financial Close Process with Oracle Solutions
- AI Agents in Oracle Fusion Apps: Driving Smarter Decisions, Faster Workflows, and Efficient Operations
- Navigating the Oracle Landscape: Emerging Trends Driving Innovation and Shaping 2025
- Supercharging Generative AI with RAG: Empowering AI with Memory, Knowledge, and Context
- Optimizing Accounts Payable: Boosting Working Capital and Efficiency with Oracle’s ERP Solution




